Step 1
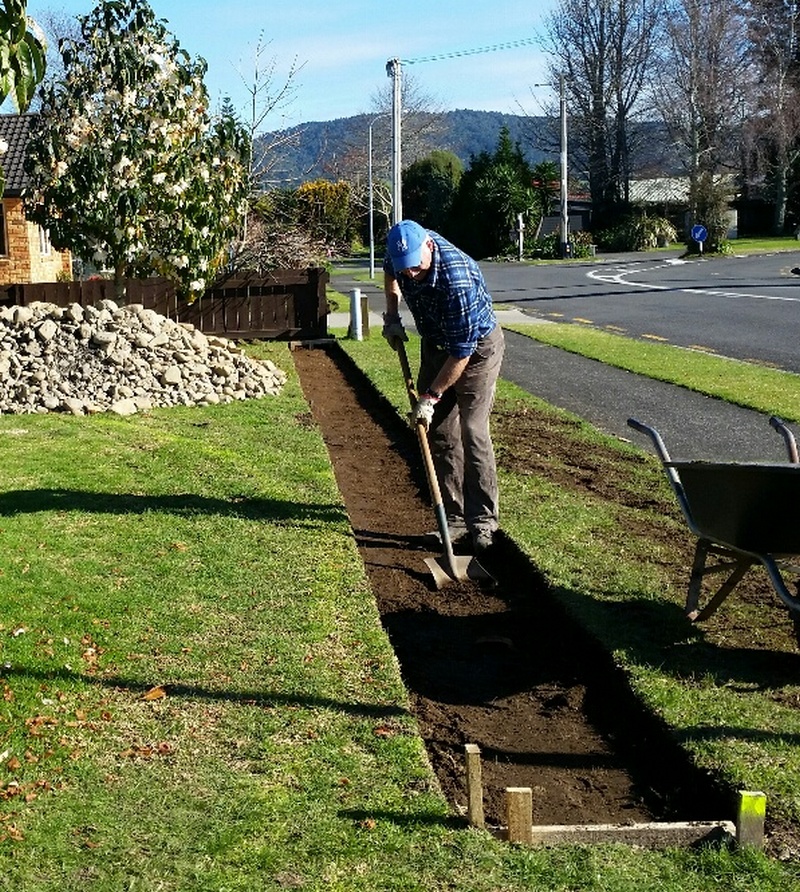
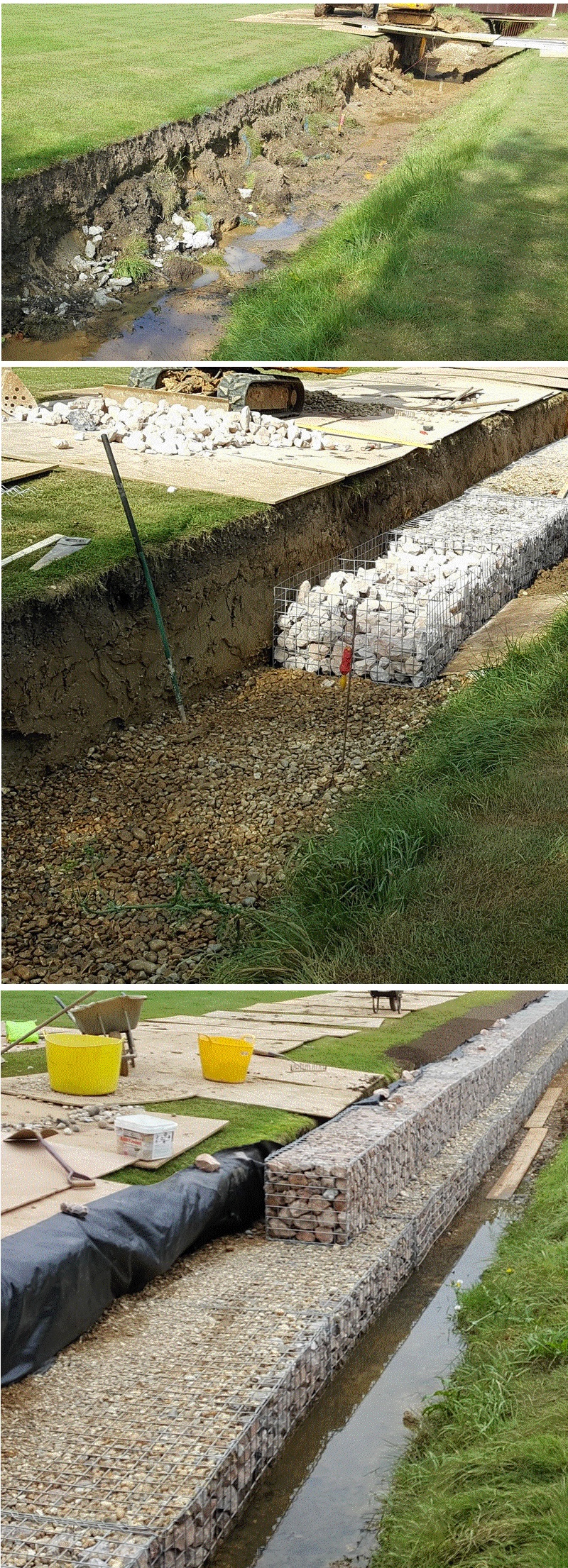
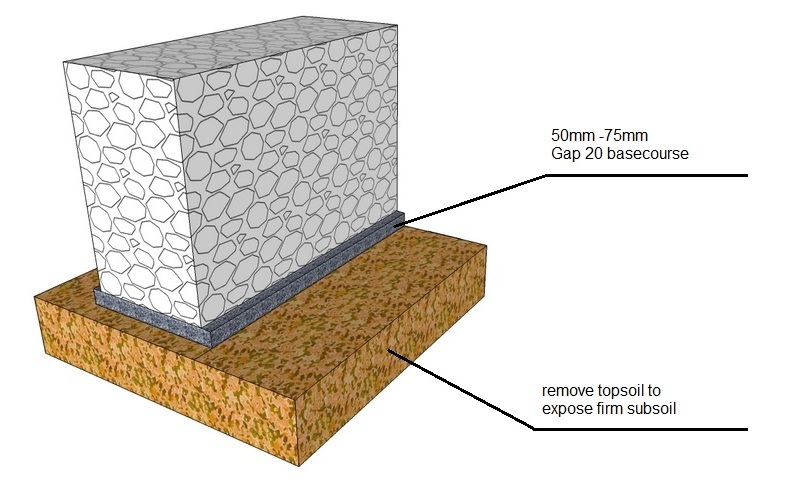
Remove topsoil and soft subsoils
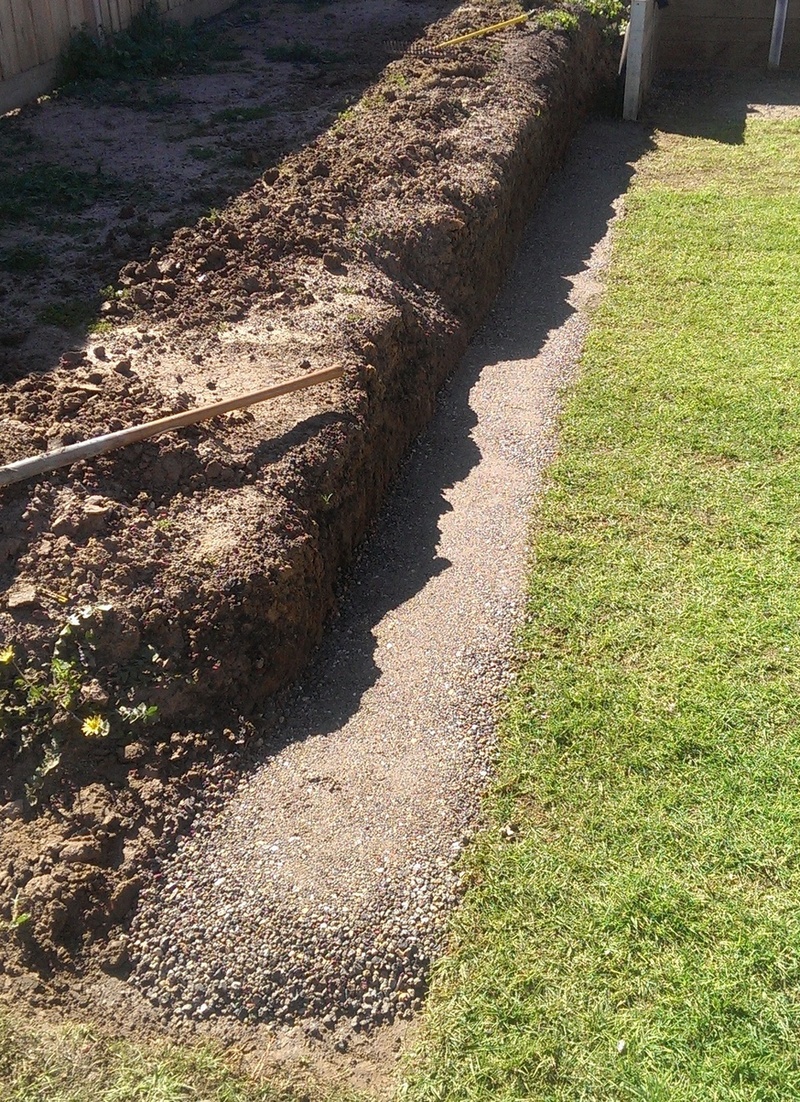
Basecourse thickness
The required thickness of basecourse, depends on the actual site subsoil conditions.
In general you will need to remove topsoil, peaty organic material, and softer subsoils. and replace these with compacted hardfill/basecourse.
If building your wall on bedrock, you may only require 25mm of basecourse, to level of the base
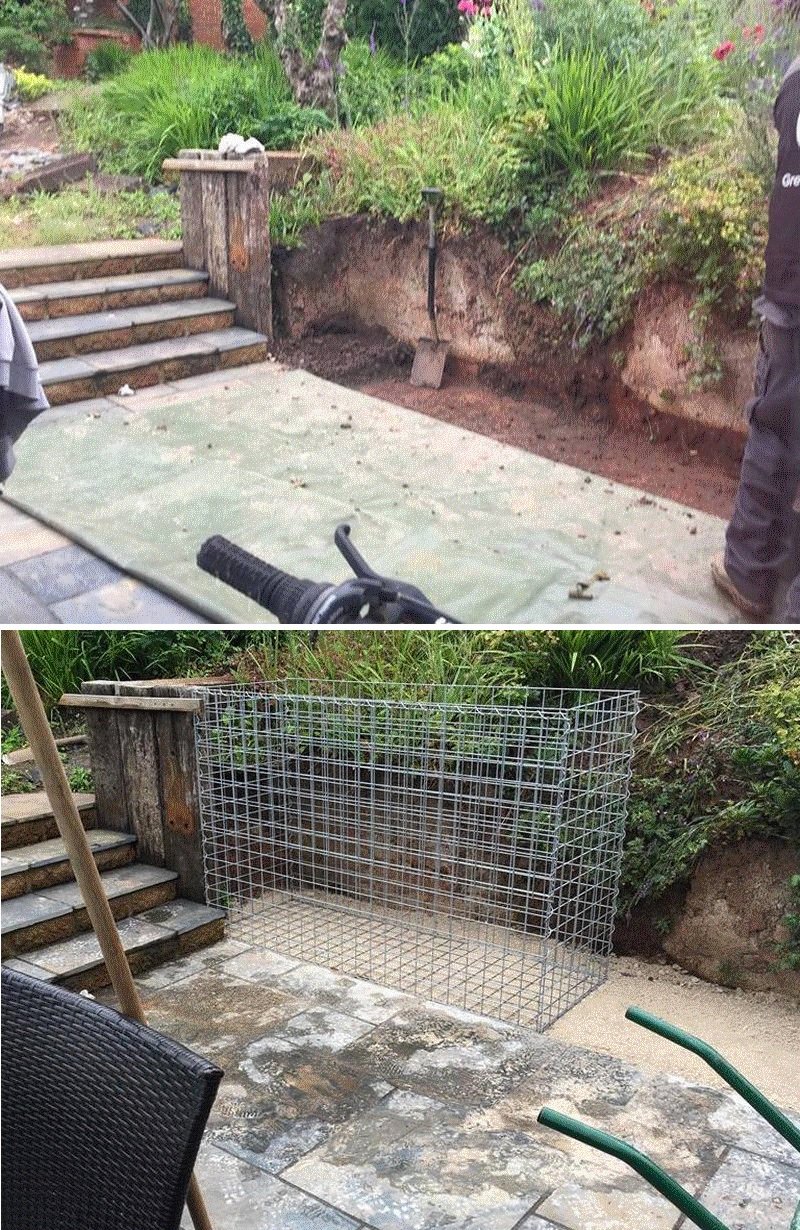
Most gabion walls do not require concrete foundations.
Foundation testing
Small non engineered retaining walls, are unlikely to require Scala Penetrometer foundation testing, which accurately measures the subsoil bearing strength.
If you are unsure about the foundation requirements, please email us or talk to a local civil engineer.
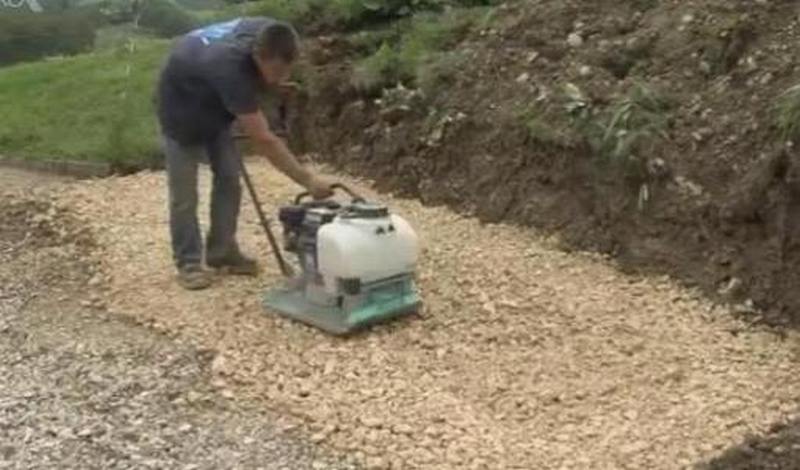
Basecourse compaction
When placing 100mm depth of basecourse or greater, you will need to use a plate compactor
Proper compaction, eliminates future consolidation, and foundation settlement.
Sand Blind
Some contractors place thin layer of sand over the basecourse for final foundation leveling.
This should not be done on sites that have high groundwater flows.
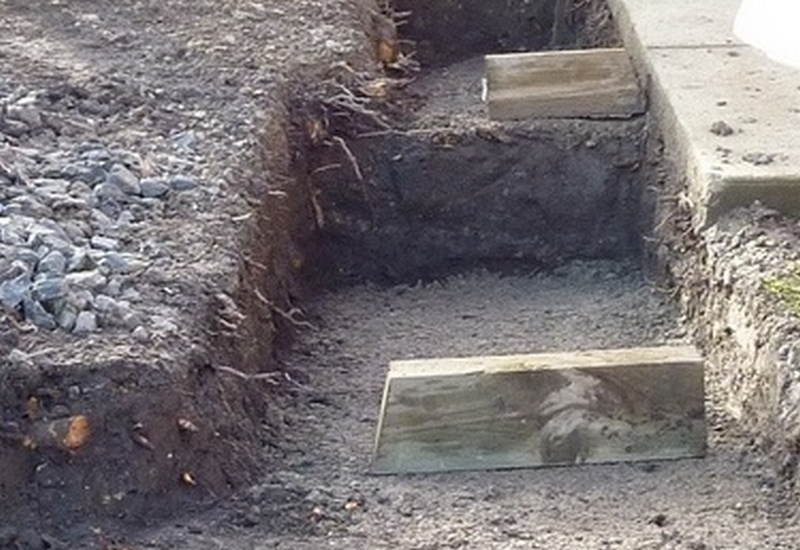
Stepped foundations
Stepping the foundation, allows walls to be built on sloping sites
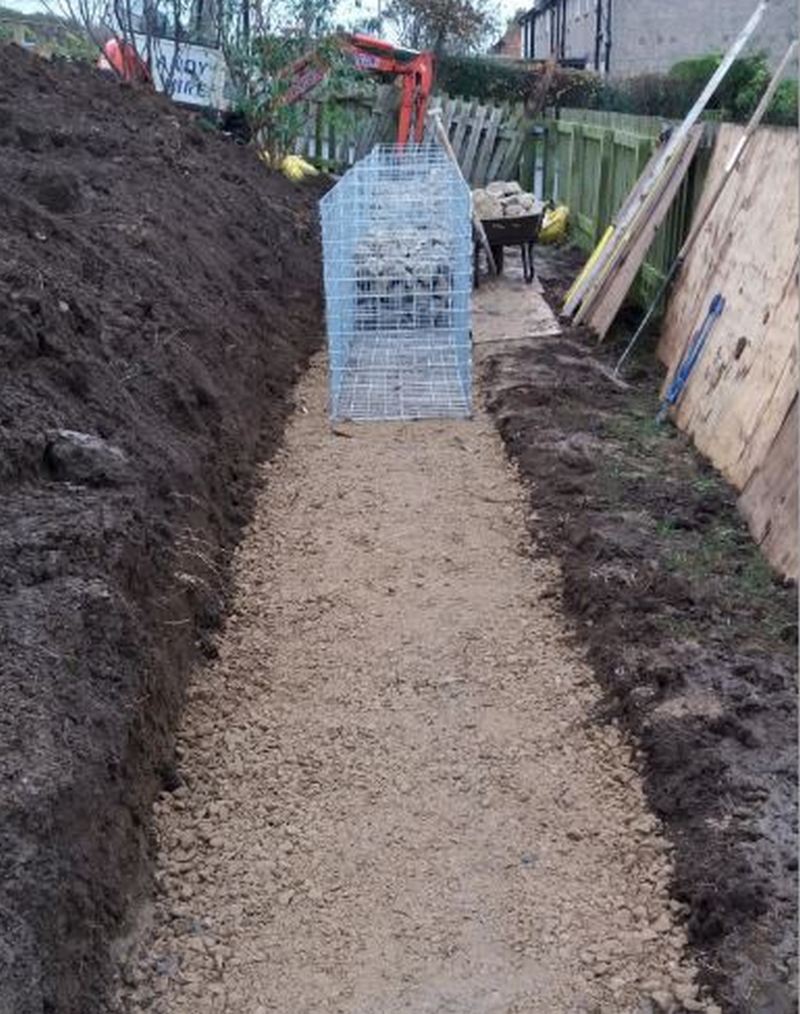
Gabion foundation examples
Stepped foundation example
Concrete ledges were cast into the bedrock,
The concrete foundations were based on the gabion basket sizes being installed.
Foundation questions
If you have any other gabion foundation questions, please email us some pics of your site with your questions.
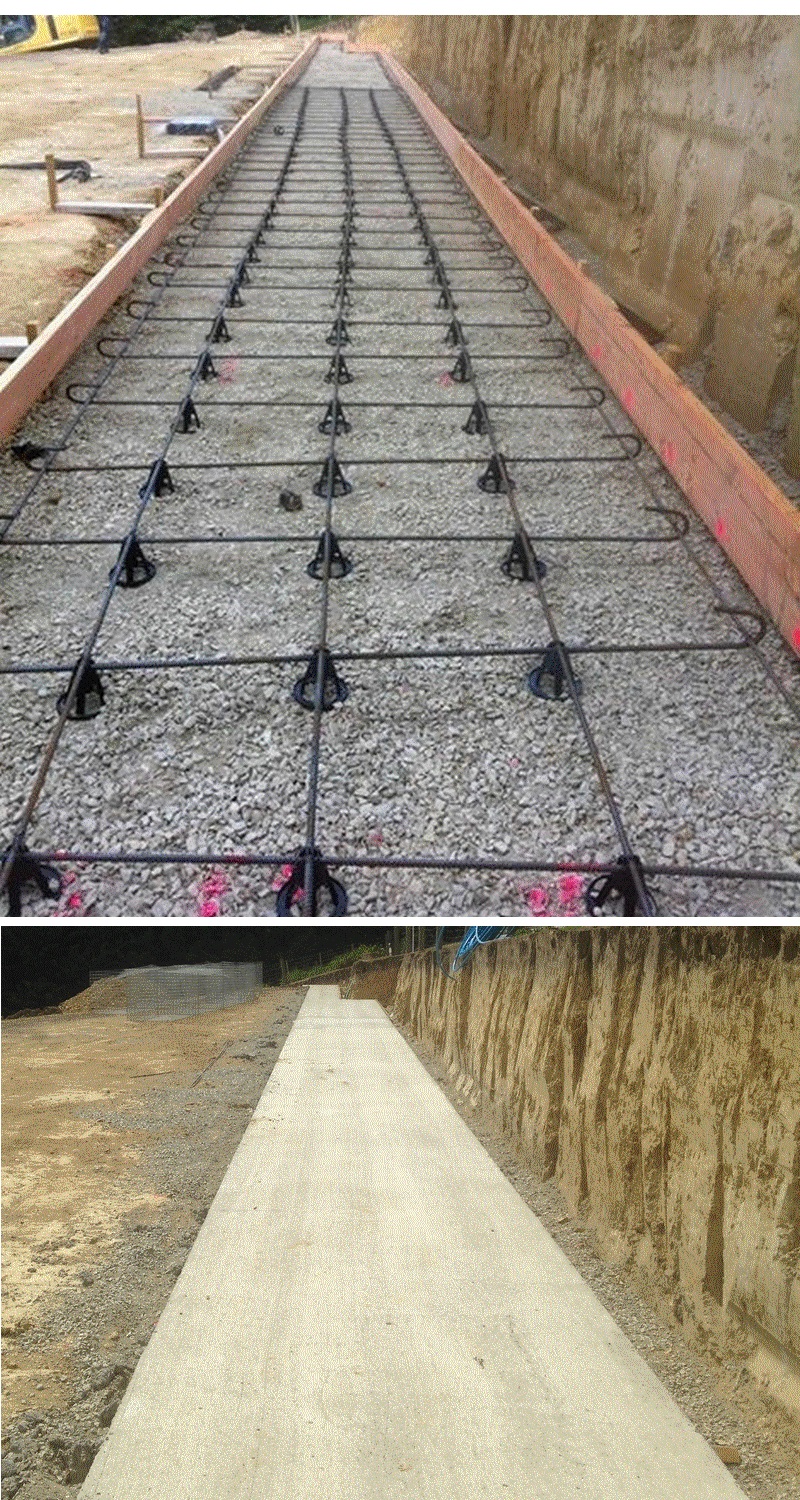
Concrete foundations
It is very rare for a gabion walls to require a concrete foundation, below is an example. If you site has groundwater issues, it may be advisable to use galv coated reinforcing steel
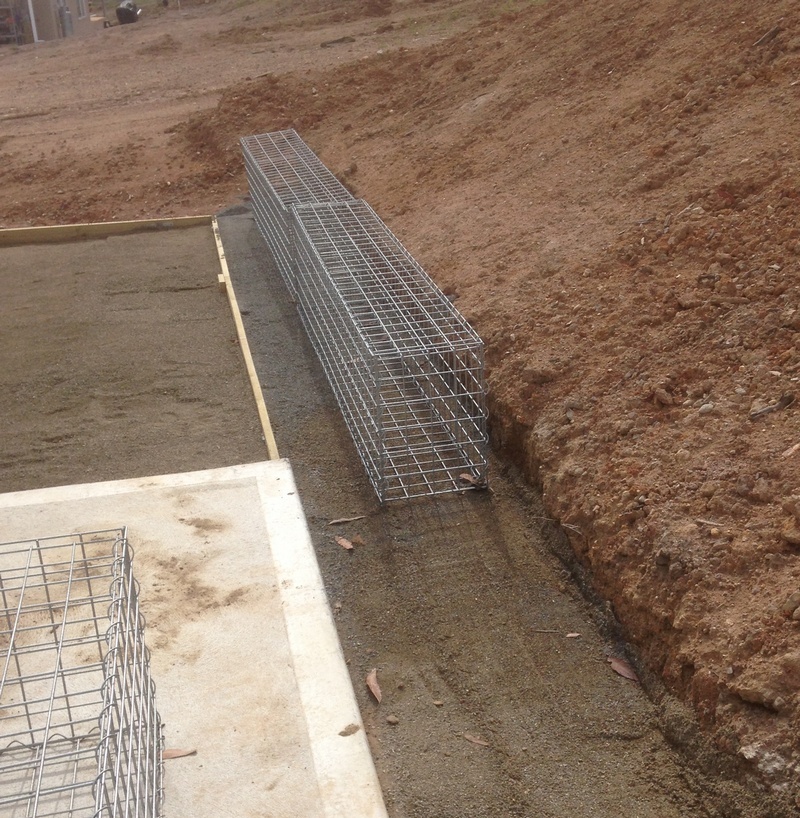
Double width base gabion
The extra width of the base gabion improves, wall stability, and reduces the bearing load on the subsoil,
Spreading the load over a larger area, allows gabion walls to be built on weaker subsoils without expensive foundations.